

Max Davies
How Audi, BMW, Honda, Mercedes-Benz, and Suzuki started out in Australia, and where they are now
14 Hours Ago
Tesla is known for its Supercharger network. But what other charging networks are there, where can you find them, and how quickly can they charge your EV?

Contributor


Contributor
A major consideration when buying an electric vehicle is where to charge it.
While most owners will charge at home most of the time, some longer trips will necessitate plugging into a public fast charger.
Unlike petrol stations, which are relatively uniform in the types of fuel offered and how fast you can fill up, the charging speed (and plug types) on offer at DC public charge points varies widely around Australia.
Tesla is well-known for its Supercharger network, reserved exclusively for owners of its cars. Other major networks include ChargeFox, which offers a network of ultra-rapid charging stations that compares favourably to the Tesla network.
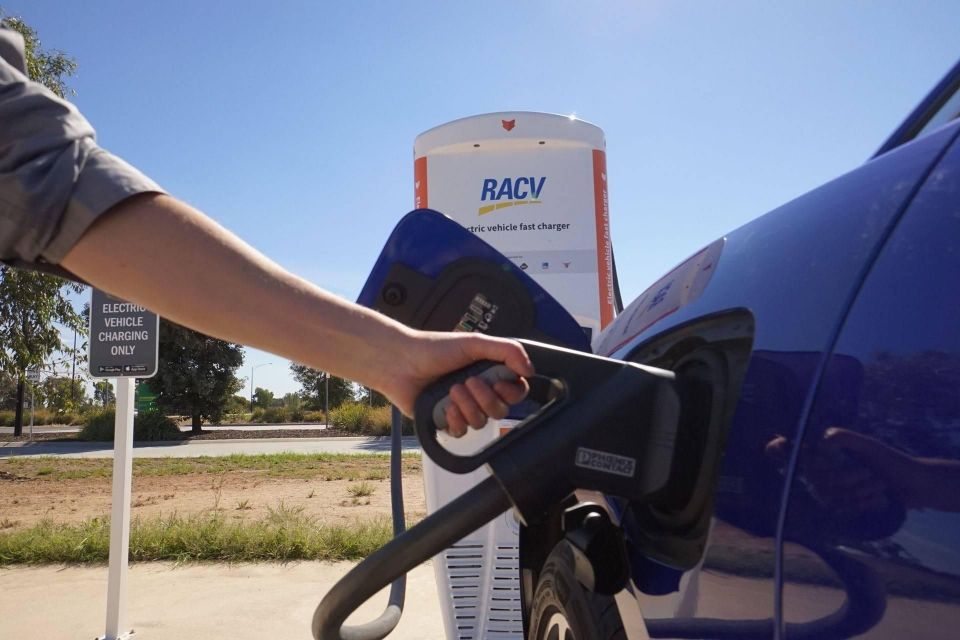
Australian Motoring Services, an umbrella for state-based automotive clubs (such as the NRMA, RACQ and RACV), is also rolling out a network of charge stations.
This story will focus on charging stations as part of a network, rather than the standalone chargers commonly found at shopping centre carparks or other chain stores.
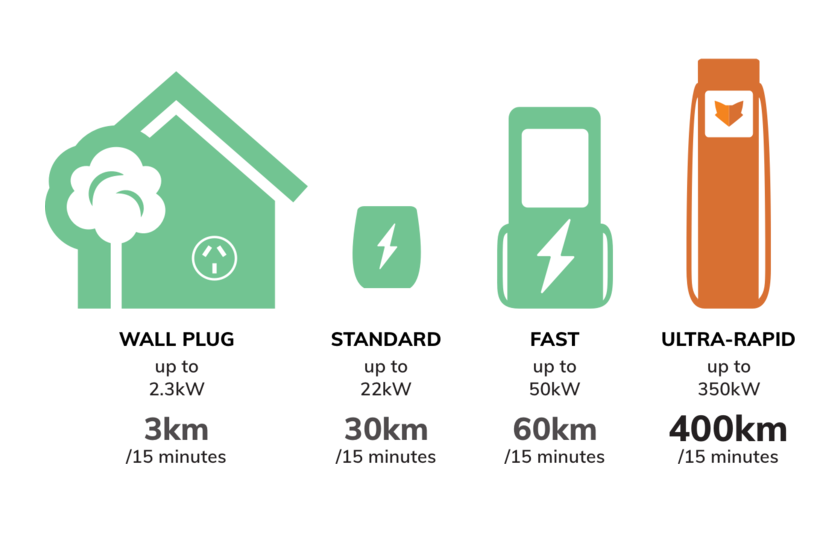
One thing to note is the difference between AC and DC charging. AC charging is what’s used to charge an electric car at home, and is significantly slower than DC charging.
Electric cars feature an onboard charger converting AC to DC power, typically at speeds under 20kW. DC chargers bypass this onboard converter by supplying DC directly, facilitating much faster charging speeds of 50kW and above.
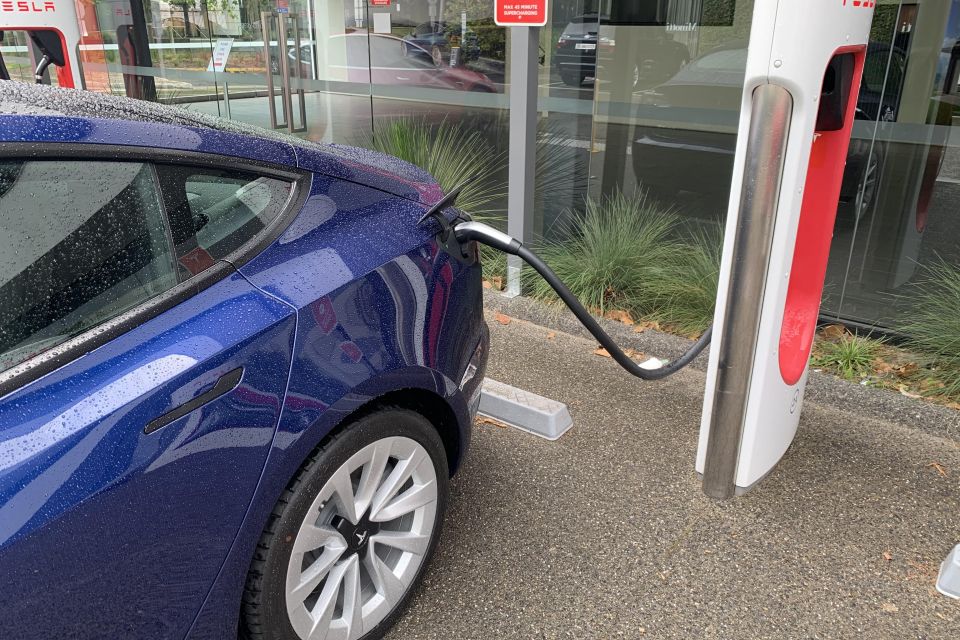
Tesla’s network consists of two types of charger. These are Superchargers, and Tesla Destination Chargers.
Compatible exclusively with Tesla vehicles, Superchargers in Australia can currently charge at a peak rate of 120kW.
Overseas, Tesla has introduced V3 Superchargers that can charge more than twice as fast, with a peak rate of 250kW.

As their name suggests, Destination Chargers are located at destinations where customers will use a parking spot for an extended period of time, such as hotels and shopping centres.
As the expectation is customers will park their cars for a longer period of time, Destination Chargers will take longer to charge a Tesla.
The output of these destination chargers varies based on location.
The current Supercharger network is spread across the Eastern Seaboard from the Sunshine Coast all the way down to Melbourne, and at regional centres such as Goulburn, Nowra, Bathurst, Bendigo, and Ballarat.
There are currently three stations (each station contains multiple plugs) in South Australia, including in Adelaide, while the west is served by one in Eaton, south of Perth.
Tesla Destination Chargers are more widespread, and feature in all Australian states and territories, including Tasmania.

Geographic spread: Primarily Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, and ACT, with three stations in South Australia, and one in Western Australia. Number: 36 Supercharger stations currently available, with another 17 planned. Note each Supercharger station may include multiple plugs. Speed: Peak charging speed of 120kW. Cost: Approximately 52c/kWh. Please note that this may vary over time and in different locations. Compatibility: Exclusive to Tesla vehicles
The state-based Australian Motoring Services have invested in various electric charging networks and companies, such as ChargeFox and Tritium, to build a network of DC rapid charging stations across the country.
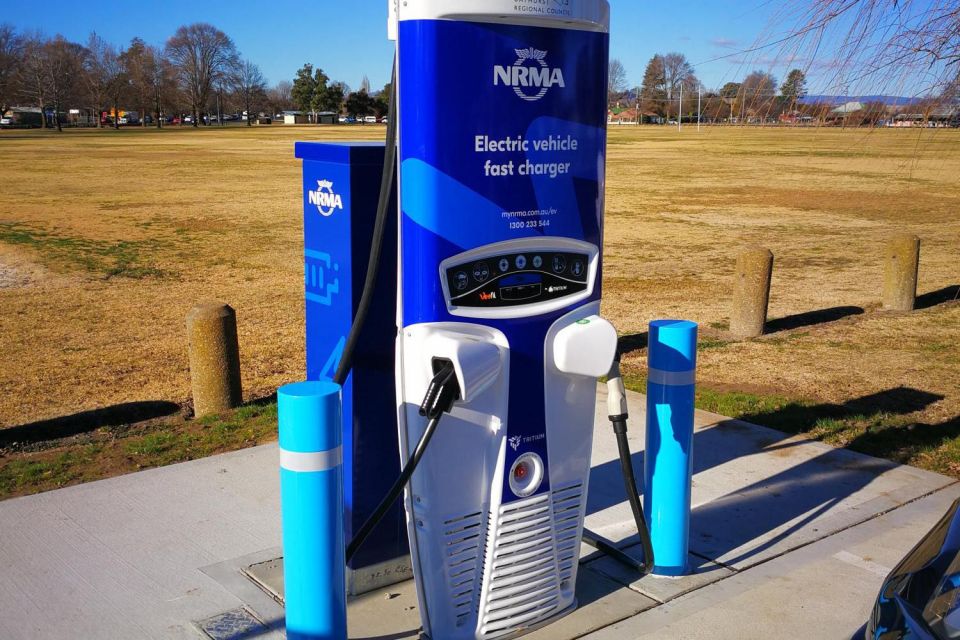
The NRMA-branded network stretches from northern New South Wales near Byron Bay down towards Albury, and west through Hay into South Australia.
It offers charging speeds up to 50kW across thoroughfares such as Sydney’s Great Western Highway, and has announced it will be partnering with the NSW Government to deliver at least an additional 20 fast chargers in key regional centres.

Queensland’s equivalent, the RACQ, is partnering with energy company Yurika and the Queensland Government to deliver 13 new charging stations on what is known as the ‘Queensland Electric Vehicle Superhighway’ (QESH) stretching from Cairns down to the Gold Coast and Coolangatta.
Geographic spread: Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, ACT, and Tasmania.
Number: More than 44 fast chargers in NSW, numbers vary in other states.
Speed: Peak charging speed of 50kW.
Cost: Varies based on state. Fast chargers are currently free for NRMA members and non-members alike (non-members are expected to be charged soon), whilst in Queensland, the QESH costs approximately 20c/kWh. AMS members may also receive discounts when using the ChargeFox EV network.
Compatibility: Most EVs that use a CCS Type 2 or CHAdeMO plug.
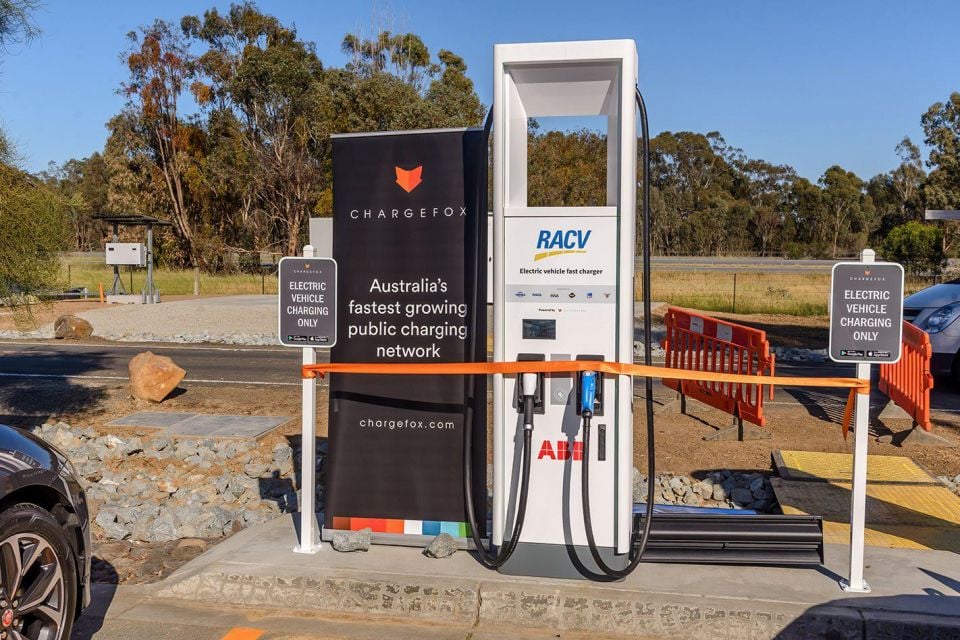
ChargeFox is a private company that offers arguably the widest fast-charging EV network in Australia. Having received investment from Greg Roebuck, founder of CarSales, Australian Motoring Services, and grants from the Victorian Government and the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, it currently has fast chargers in every state and territory except the Northern Territory.
Apart from its wide availability, ChargeFox is notable for offering some of the fastest charging speeds available in Australia, with certain stations featuring 350kW ultra-fast DC chargers designed by Australian company Tritium.
Notably, these ultra-rapid chargers are all powered by renewable energy sources.

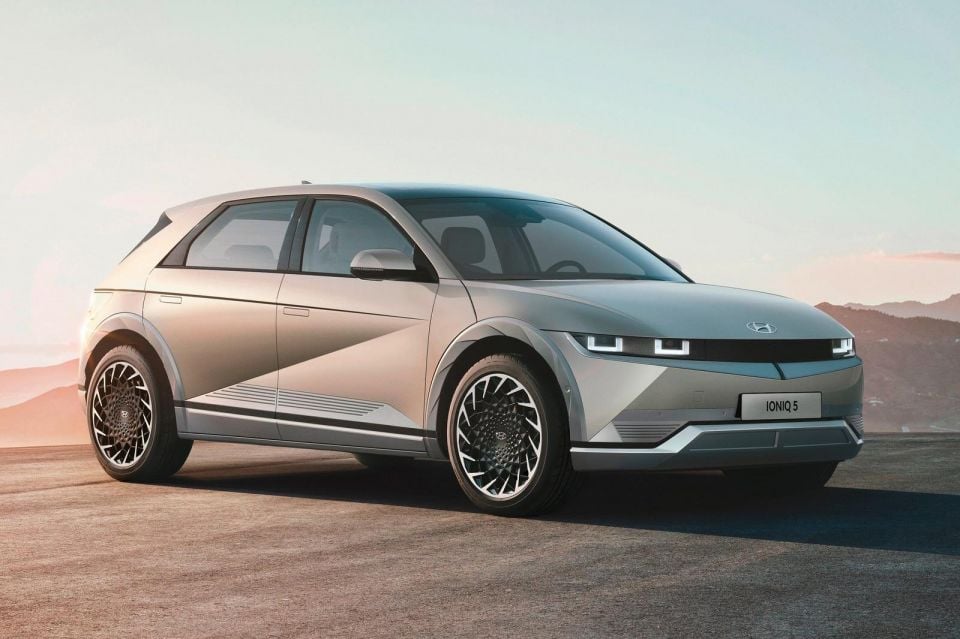
Certain electric vehicles that make use of an 800V architecture, such as the Porsche Taycan and Hyundai Ioniq 5, can take advantage of these high charging speeds to quickly charge from 10 to 80 per cent in less than 30 minutes.
The ChargeFox network also features a range of 50kW and 100kW fast charging stations.

Geographic spread: Every state and territory except the Northern Territory Number: 22 ultra-rapid (350kW) charging stations, over 1400 chargers in total Speed: Up to 350kW peak at an ultra-rapid charging station. Other chargers have peak speeds of 22kW, 50kW or 100kW. Cost: Varies based on location and charger speed, but ranges from 25c/kWh to 40c/kWh. Some chargers may use a compound fee structure that combines a lower per kWh charging rate with an additional per minute fee. Compatibility: Most using a CCS Type 2 or CHAdeMO plug.
The networks described above are not the only players in Australia. Smaller, but rapidly expanding, competitors include Evie Networks, ChargePoint and EVUp.


Max Davies
14 Hours Ago


William Stopford
14 Hours Ago


Derek Fung
15 Hours Ago


Max Davies
22 Hours Ago


William Stopford
2 Days Ago


Ben Zachariah
2 Days Ago